What are Immutable classes/objects in java?
Today, in this
tutorial we will learn what immutable objects are, how we can create immutable
objects and what are the advantages of immutable objects. First, let’s
understand what does immutable mean.
What is an immutable
object?
An immutable object is
an object whose internal state remains constant after the object is created. In
other words, if an object is created as immutable then that object guarantees
that the object will behave the same entire lifetime.
Final vs Immutable.
Final – final can be class, variable or method
in java. Final modifier ensures that once the variable is declared as final its
value cannot be modified. If the class is declared as final then it can be
extended.
Immutability - In simple terms, immutability means that
it does not change over time or that it cannot be changed. In Java, we know
that String objects are immutable, which means that we cannot change anything
in existing String objects.
Difference between Final
and Immutable
1. Final means that you
cannot change the object's reference to point to another reference or another
object, but you can still mutate its position (using the setter method). Where
immutable means that the true value of an object cannot be changed, but its
reference to another can be changed.
2. The final modifier is
applicable for variables, not for objects, while immutability is applicable for
objects, not for variables.
3. Final ensures that
the address of the object remains the same, while the immutable suggests that
we cannot change the state of the object once it is created.
4. By declaring the
reference variable as final we are not going to obtain any nature of
immutability but we can make any kind of change to the corresponding objects
and we cannot reassign the reference variable to any new object.
String class –
The string is the most
used class in java. In java, the String class is made immutable. There are some
reasons why the String class is made immutable in java:
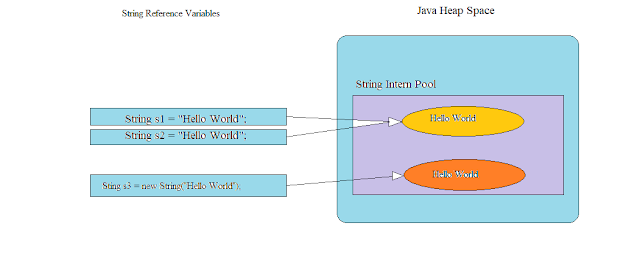
1. String pool – Reusing the String literal by caching them saves a lot of heap space as different String variables refer to the same String object in String pool. The same service is given by String literal pool also.
The Java string pool is the special memory area where strings are stored by the JVM. Because of Sting immutability, the allocated memory is optimized by JVM by storing only one copy of each literal String into the pool. This process is called interning.
Due to the presence of a string pool in the preceding example, two different variables are pointing to the same string object from the pool, thus saving significant memory resources.
2. Security – Strings are used to store sensitive information like username, password, network connections etc,
If the strings were mutable, by the time we run the update, we cannot be sure that the string we receive, even after running the security checks, is secure. The untrusted calling method still has the reference and can change the String between integrity checks. So our query is prone to SQL injections in this case. Therefore, mutable strings could cause security degradation over time.
In general, immutability comes to our rescue in this case because it is easier to operate with sensitive code when the values do not change. After all, there are fewer collations of operations that could affect the result.
3. Synchronization – The immutability ability of String make them thread-safe automatically. Therefore, immutable objects can generally be shared on multiple threads running simultaneously. They are also thread-safe because if a thread changes the value, then instead of changing the same, a new string will be created in the String pool. Therefore, the strings are safe for multiple threads.
4. Hashcode - We can see that String class is used in Data structures like HashMap, HashTable, HashSet etc, The String immutability guarantee that their value will not change. So, to facilitate the hashing mechanism, the hashCode() method is overridden in String class. Hence, the hash code is calculated in the beginning and the same will be returned every since.
On the other hand, mutable String has the potential to lose the value object in the map during insertion and retrieval, if the content of the String is modified.
These were some of the
reasons why the String class is made immutable in java. We can create an
immutable object using programming also. Let’s see how we can create an
immutable class in java and how we can use immutable objects.
How to create user defined immutable class?
Java provides the
facility to the users to create our immutable class. Here are some of the rules
that we have to follow while creating the immutable class:
1. Declare the class as final so the class
extension can be restricted.
2. Make the data variables as private so that
outside access should be restricted.
3. No setter methods should be provided.
4. Mutable fields should be made final so that
their value should be assigned only once.
5. Initialize all fields using a constructor that performs
a deep copy.
6. Make sure you always return a clone copy of the
field, and never return the instance of the actual object.
Let’s create our own immutable class following the above steps:
Conclusion –
Immutable classes propose
lot of advantages, especially when used correctly in a multi-threaded
environment. The only downside is that it consumes more memory than the
traditional class because with each change a new object is created in the
memory but, a developer should not overestimate the memory consumption, because
it is negligible compared to the advantages offered by these types of classes.
Finally, an object is
immutable if it can present a single state to other objects, no matter how and
when they name its methods. If so, it is safe by any definition of thread-safe.



0 Comments